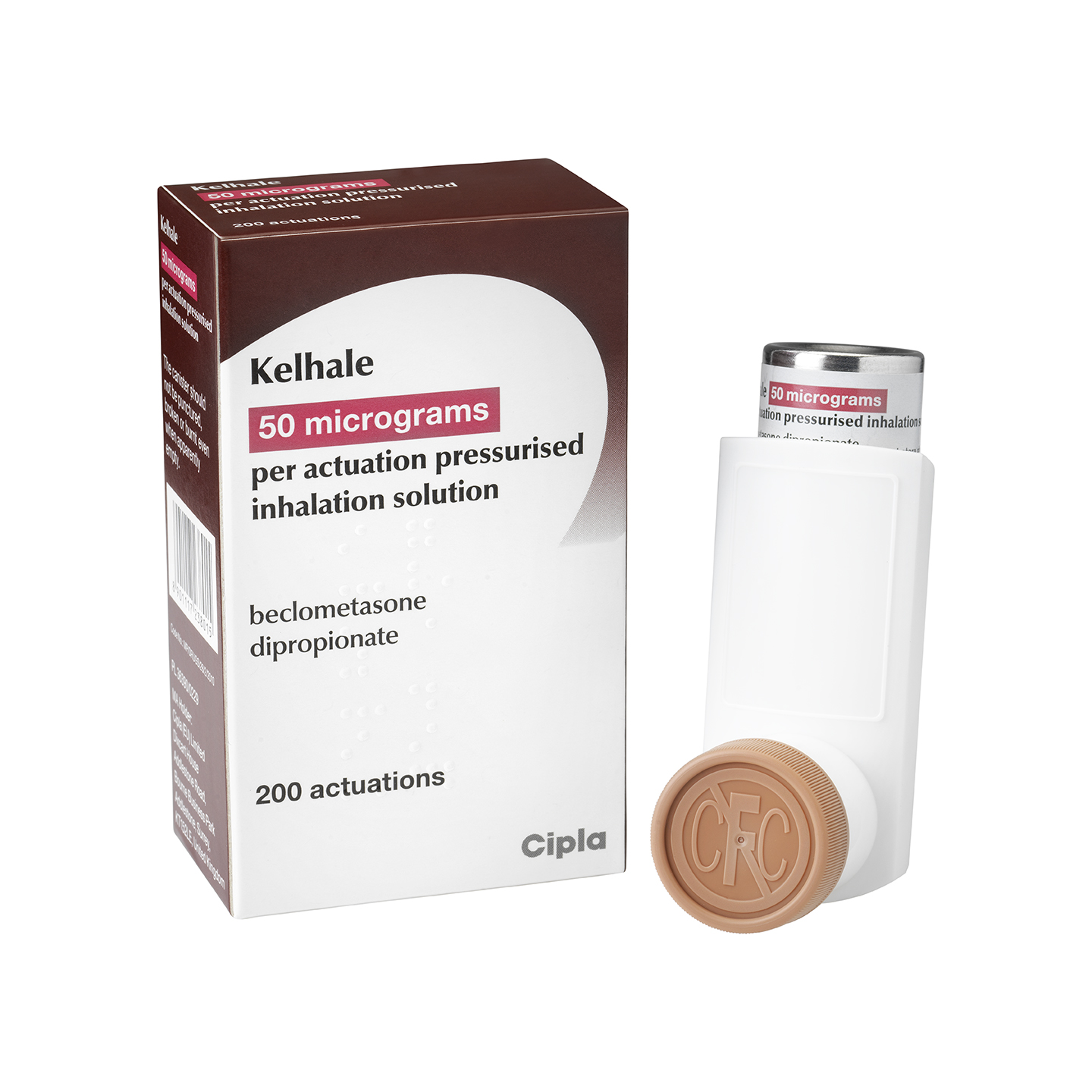
Kelhale
Indication1,2
Kelhale is indicated for the prophylactic management of mild, moderate or severe asthma, in adults over 18 years of age. It is not licensed for use in those under 18 years of age.1,2
Kelhale can help patients maintain a lower steroid dose than non-extrafine formulations3
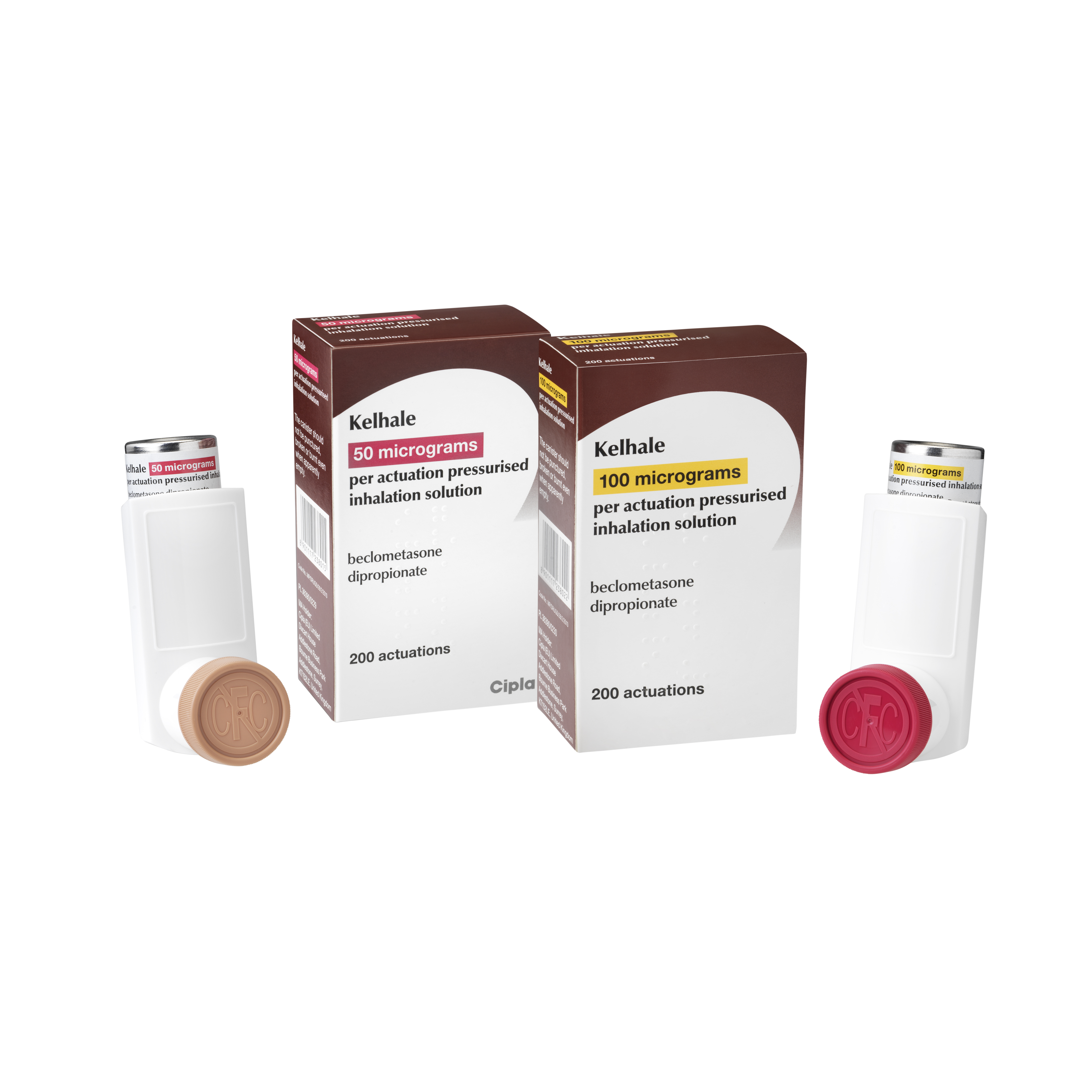
Kelhale is available in two strengths: 50 and 100 micrograms of extrafine beclometasone1,2
It is supplied as a pressurised metered dose inhaler and is suitable for use with an AeroChamber Plus spacer*.1,2
*AeroChamber Plus is a trademark of Trudell Medical International.
What is the active
ingredient in Kelhale?1,2
Kelhale is available in two presentations:
- 50 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate per actuation pressurised inhalation solution
- 100 micrograms of beclometasone dipropionate per actuation pressurised inhalation solution
Kelhale Dosing1,2
Adults 18 years of age and older1,2
Starting and maintenance dose
It is important to gain control of asthma symptoms and optimise pulmonary
function as soon as possible. When patients’ symptoms remain under satisfactory
control, the dose should be titrated to the lowest dose at which effective
control of asthma is maintained.
To be effective inhaled Kelhale must be used
on a regular basis even when patients are asymptomatic.
Therapy in new patients should be initiated at the following doses:
- Mild asthma: 100 to 200 micrograms per day in two divided doses.
- Moderate asthma: 200 to 400 micrograms per day in two divided doses.
- Severe asthma: 400 to 800 micrograms per day in two divided doses.

Kelhale dose
indicator1,2,4,5
On the back of the Kelhale inhaler, there is a dose indicator to help your patient keep track of the amount of medicine left in the canister.
The inhaler contains 200 doses. As your patient uses the inhaler, the number on the back will reduce from 200 to 0. Every dose your patient takes counts, but the indicator changes only every 20 doses.
Your patient should request a replacement inhaler when there are 40 doses remaining.
When the dose indicator displays 0, your patient should stop using the inhaler. This is because any medicine left in the canister may not be a full dose.


